Tantalum carbides (TaC) are a family of binary compounds of tantalum and carbon with the empirical formula TaCx, where x generally ranges between 0.4 and 1. They are very difficult, breakable, refractory ceramic materials with metallic conductivity. They appear as a brownish-grey powder and are usually processed by sintering.
As an important cermet material, tantalum carbide is used commercially in tool tips for cutting applications and is sometimes added to tungsten carbide alloys.
Based on purity and measurement conditions, tantalum carbide’s melting point was estimated to be approximately 3,880 °C; this value is the highest among binary compounds. Only hafnium-tantalum carbide is estimated to have a higher melting point of 3,942 °C. However, new tests conclusively demonstrated that TaC actually has a melting point of 3,768 °C, while both tantalum-hafnium carbide and hafnium carbide have higher melting points.
Preparation of tantalum carbide
TaCx powders of the desired make-up are prepared by heating up a blend of tantalum and graphite powders in a vacuum or in an inert gas atmosphere (argon). Heating is performed using a furnace or arc melting unit at a temperature of approximately 2,000 °C. Another technique is the reduction of tantalum pentoxide with carbon in a vacuum or hydrogen atmosphere at temperatures of 1,500–1,700 °C. This approach was made use of to obtain tantalum carbide in 1876, but it lacked control over product stoichiometry. The production of TaC directly from elements via self-propagating high-temperature synthesis has been reported.
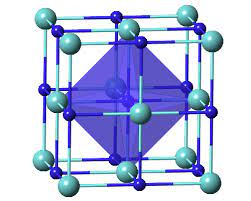
Crystal structure of tantalum carbide
TaCx compounds have a cubic (rock salt) crystal structure with x = 0.7–1.0; the lattice parameter increases with x. There are two main crystal forms of TaC0.5. The more stable one has an inverse cadmium iodide-type triangular structure that, when heated to about 2,000°C, transforms into a hexagonal lattice in which the carbon atoms have no long-range order.
Properties of Tantalum Carbide
The tantalum and carbon atoms bonding in tantalum carbide is a complex mixture of ionic, metallic and covalent components. As a result of the strong covalent component, these carbides are really tough and weak materials. As an example, TaC has a microhardness of 1,600– 2,000 kg/mm2 (~ 9 Mohs) and an elastic modulus of 285 Grade point average, while the equivalent worths for tantalum are 110 kg/mm2 and 186 GPa.
Titanium carbide has metallic conductivity, both size and temperature dependent. TaC is a superconductor with a fairly high transition temperature TC = 10.35 K.
The magnetism of TaCx changes from diamagnetic for x ≤ 0.9 to paramagnetic for larger x. Though HfCx has the same crystal structure as TaCx, it is observed to have the opposite behavior (paramagnetic transition with increasing x).
Applications of Tantalum Carbide
Tantalum carbide has important applications in materials science. Tantalum carbide is widely used as a high-temperature structural material due to its high melting point, hardness, and corrosion resistance. For example, tantalum carbide can be used to make high-temperature alloys and refractory materials and to make stoves, aerospace engine components, and high-temperature tools. Additionally, tantalum carbide can also be used to make wear-resistant materials, such as automobile brake pads, knives, etc.
Tantalum carbide also has important applications in the electronics industry. Tantalum carbide has good electrical conductivity and high temperature stability and can be used to make electronic components and resistors. For example, tantalum carbide films can be used to make capacitors and tantalum carbide powder can be used to make resistors. Furthermore, tantalum carbide can also be used as a semiconductor material for the manufacture of high-power electronic devices and optoelectronic devices.
Tantalum carbide is also used in the chemical industry. Tantalum carbide has good chemical stability and high temperature corrosion resistance and can be used to manufacture chemical equipment and catalysts. For example, tantalum carbide can be used to make chemical reactors, pipes and valves, and can be used to make ammonia synthesis catalysts and petrochemical catalysts.
Tantalum carbide also has potential applications in the medical and bioscience fields. Because tantalum carbide has good biocompatibility and bioinertness, it can be used to manufacture artificial joints,
Medical devices such as dental implants and orthopedic implants.
Tantalum carbide has a wide range of uses in fields such as materials science, electronics industry, chemical industry, medical and biological sciences. Its excellent performance makes it play an important role in these fields. With the sustainable advancement of science and technology, the application prospects of tantalum carbide will be broader.
Supplier
TRUNNANOÂ is a supplier of tantalum carbide with over 12 years experience in nano-building energy conservation and nanotechnology development. It accepts payment via Credit Card, T/T, West Union and Paypal. Trunnano will ship the goods to customers overseas through FedEx, DHL, by air, or by sea. If you are looking for high quality tantalum carbide please feel free to contact us and send an inquiry.